What Is a 529 Plan? And Why Is It So Important to Have One to Save Money for College?
Friday Apr. 21st, 2023

Saving money for a child's college seems like a daunting task, especially when you have to pay bills for rent, utilities, cars, and groceries. Using a $25 loan instant app to save small amounts every week is not an option. But there are a few plans, like Plan 529, that help you save for your child's education costs much earlier, so your child may not have to take out student loans later. In this article, we'll look at how to fit a 529 plan into your savings strategy.
What Is a 529 Plan?
Plan 529 is a savings plan that helps families set tax-deferred money for future education expenses. Earning in a 529 plan is tax-free as long as it is used for education expenses, which also include tuition, room and board, books, and other related expenses. Typically, 529 plans are offered by states or educational institutions.
There are two types of plan 529:
● College savings plans: this type of plan allows you to invest your money in after-tax investments to increase funds over time to pay for future education expenses. The sooner you open a savings account, the longer the funds will grow. You do not have to attend state universities in most states to use the 529 savings plan. But also, do not forget that this is an investment account, so it is associated with some risks, due to which you can lose your money.
● Prepaid tuition plans: this plan allows you to pay for tuition in advance at today's prices. This is usually offered by public colleges and state universities. I would like to add that the federal government does not guarantee these plans, but some states promise to provide funding even if the program runs into financial difficulties. You can pay using this type only for tuition and fees, room and board are not included in this payment. Unfortunately, not all colleges and universities participate, which also limits your child's future choices.
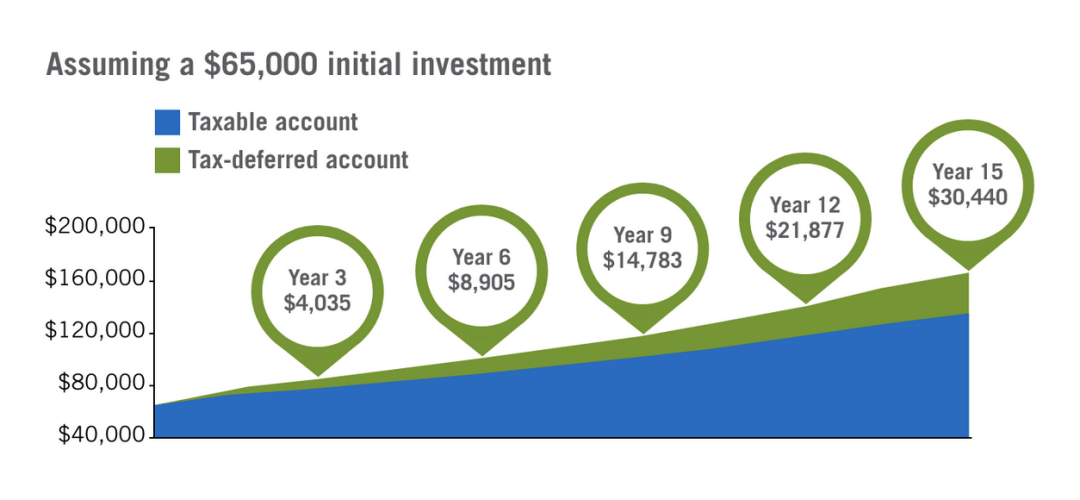
But what about tax-deferred potential? Thanks to the 529 plan, it has more growth potential than a taxable account. We can clearly see this in the graph below. This data is just an example; we don't count any expenses people have. The graphic is presented only for comparing two types: 529 plan and taxable investment account.
How Does a 529 Plan Work?
To open a 529 plan, you will need to choose a plan provider and open an account. Now let's look at how to choose your plan and the next steps which you will follow to learn how to start a 529 plan.
● Step 1: The first thing to do is choose your plan. First, all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and a fair number of brokerage firms offer the 529 plan. You should investigate each benefit to see which is best for your case. It is worth remembering that at least 30 states provide a tax deduction for contributions to this plan, but the rules are different for everyone. State-run plans may have lower limits than those offered by brokerage firms.
● Step 2: The next thing to consider is whether you will open this plan for yourself or, for example, a child or other relative. Because in that case, you'll need information for both of you. First of all, this is your social security number, date of birth and address, and banking information, including your account number and routing number. But if you also open for, for instance, a child, you will also need his social security number and date of birth.
● Step 3: Now we'll move on to enrolling on your state's or brokerage's 529 plan web page. On it, you will see the button "Enroll now" or "Open an account." The order in which information is requested is different for each state. Still, in any case, you will need to enter personal information such as name, date of birth, address, phone number, social security number, and your child or relative if you are not opening this account for yourself.
● Step 4: After you have entered your personal information, you should choose which account you want. Several options will be available to you, depending on which state or brokerage firm's plan you choose.
● Step 5: And so when your plan is selected, you can add funds. The minimum deposit varies from $0 to $3,000, depending on your chosen plan. Each state sets its own minimum deposit and other requirements. Brokerage-administered accounts vary similarly.
● Step 6: The main advantage of the 529 plan is that the money you invest will be invested and will bring you income over time. That's why you also need to choose how to invest your deposits. You can also divide your contribution into several parts and place them in different accounts. For example, you could put 30% of your investment in an index fund, 50% in an aggressive target-date fund, and 20% in a conservative fund.
Why Is It So Important to Save Money for College?
Plan 529 provides several benefits to help families pay for their education costs. I would like to consider several reasons why this is contemplated important:
● Any income in the account is tax-free; withdrawals for qualifying education expenses are also tax-free. This helps account holders save more money over time.
● These plans can be used to pay for the cost of education at any eligible institution, including four-year colleges, community colleges, graduate schools, and so on. This provides families with the choice of the appropriate school for the student.
● More often than not, plans have low minimum investment requirements, making it easy to save money for college, no matter your financial situation.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, a 529 plan is a valuable investment tool that can help families save for the high cost of higher education and help ensure that their student has the financial resources they need to succeed. With tax-advantaged savings, flexibility in school choice, low minimum investment, and the ability to receive gifts from others, a 529 plan can provide families with a reliable way to save for college and ensure their student has the financial resources they need to succeed. If you are considering saving for your child's education, a 529 plan is definitely worth exploring as an option.
| Tweet |